Some people handle interpersonal conflict with dialogue. Don't you wish I were one of those people?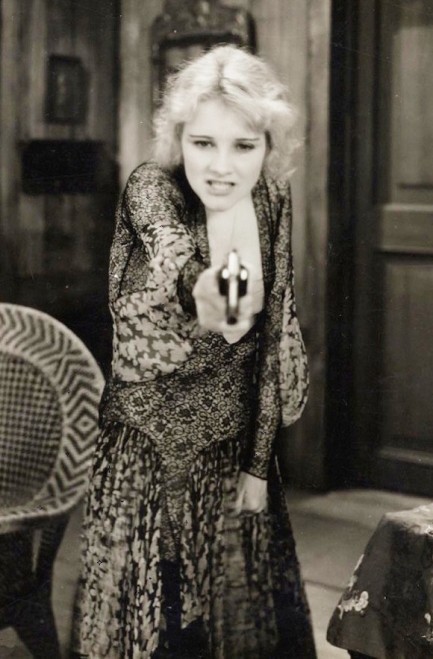 
This rather threatening photo shows U.S. pre-Code actress and former Ziegfeld Girl Jeanne Eagels seeming to gleefully aim for the gonads. She goes way back, having made her first screen appearances in 1913. She also died very young, of the oldest of Hollywood bugaboos, an overdose, a year after this photo was made. It was shot as promo for her drama The Letter in 1929.
 In this instance it's fine to Strain your eyes.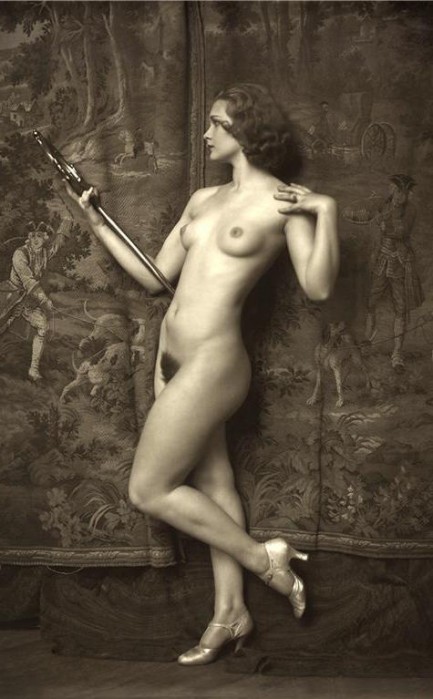 
This rather awesome photo shows U.S. actress, singer, and dancer Drucilla Strain, a Ziegfeld Girl and Broadway performer whose career ran from 1929 to the mid-1940s. The date given on this everywhere online is 1920 but that's wrong. She was a child then. The image is probably from 1930 or 1931, which was right around the time her show business career was getting off the ground. The photo—again, rather awesome—was made by famed lensman Alfred Cheney Johnston, part of a trove of unseen studio nudes unearthed after his death in 1971.
 Pearls sometimes complete an outfit, but it's the girl that always completes the pearls.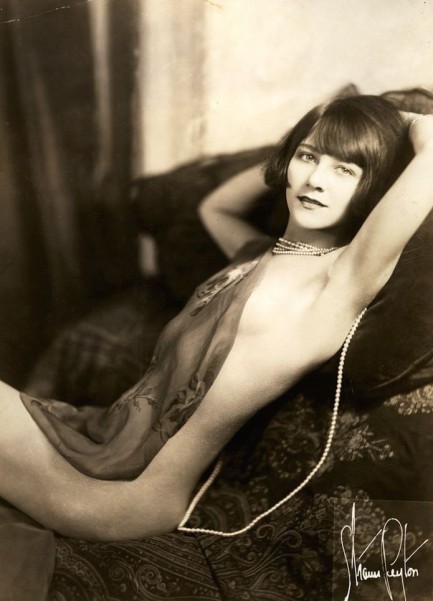 
Anastasia Reilly began her show business career tap dancing in New York City at age fourteen, by seventeen was nationally famous as a Ziegfeld Girl, and in this Strauss-Peyton (Benjamin R. Strauss and Homer Peyton) image is on top of the world in a $50,000 string of pearls. That would be about $680,000 today, which sounds like a lot until you learn some pearl necklaces top $2 million, including an $11 million ruby-studded collar that once belonged to Elizabeth Taylor. The above shot was made when Reilly was appearing in the Ziegfeld musical Louie the 14th, which ran for more than three-hundred performances at the Cosmopolitan Theatre through most of 1925. Her role was minor, but we daresay her visual impact was major, even in costume.
 A new woman for a new era. 
This issue of Paris Magazine features a beautiful Louis-Charles Royer cover of Ziegfeld star Claire Luce, one of the most popular celebrities of her time. Her heyday was the 1920s and ’30s, a period during which—though this is little remarked upon today—substantially more women began to have sex before marriage. By the time the first surveys took place in the 1940s about 50% of women admitted to having pre-marital sex. Anecdotally, during the 1920s probably at least one in four women had sex as singles. Claire Luce was a pioneer of the female right to choose. A mere eight-year span of her diary describes sixty lovers. Luce very much personifies a seismic shift in the values of Western women. Many scholars say it happened because they moved into the university and the workplace around that time, and that was indeed an important factor because it brought women and men into mutual contact outside of family and church situations. But it’s clear the prime mover was the trauma of World War I and the loss of 37 million lives in a conflict that taught those who came of age around then that life could be short and joy could be fleeting. This factor is nearly always downplayed in studies of that time, though we have never understood why. It is too obvious? Even with their numbers increasing, relatively few women were in the university and workplace. But virtually no Western family went untouched by the war. Those 37 million deaths reached deep into every town, every enclave, every social class. Nearly everyone had lost a father, a brother, an uncle, or at least a family friend. And if a loved one actually survived battle, they often returned to preach the futility of war to the generation below them—or by their mere broken presence serve as a warning. Ernest Hemingway captured this in The Sun Also Rises, which focuses on Jake, prevented by a war wound from having sex, and Lady Brett, who loves Jake but must constantly seek lovers elsewhere.
Of course, there are many factors behind any social shift, but rapid change typically derives from chaos. Ask any neo-con or disaster capitalist. The primary effect of war or warlike events upon society is to alter how it views life, death, and personal freedom. In the past, the spectre of death made people want more freedom to live as they saw fit; in our present era, traumatic events have resulted in people agreeing to sacrifice their personal freedom (thanks to powerful suggestions and hard work by opportunistic governments).
Anyway, just an interesting digression concerning Paris Magazine’s cover star. Like predecessors such as Dorothy Parker, and peers like Tallulah Bankhead, she was a sexual trendsetter, a new type of woman for a radically reordered Western world. She’s also about as pulp as it gets. We may get back to Claire Luce a bit later, but in the meantime we have a bunch of interior scans from Paris Magazine below, and more issues available at the click of a mouse. This edition, number 34, appeared in 1934.             
 Are you serious? You call that thing a nose?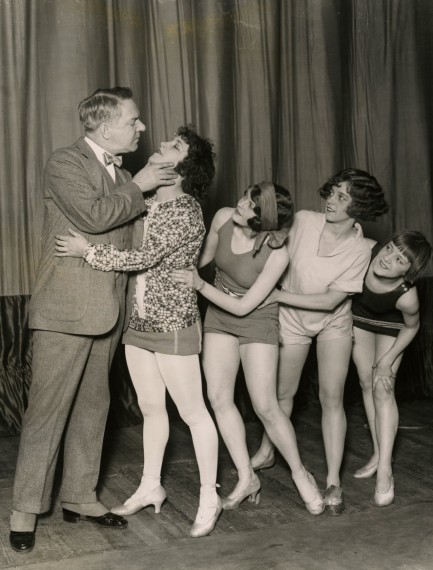 
Comedian W.C. Fields, née William Claude Dukenfield, jokes around with chorus girls Helen Ellsworth, Helene Sheldon, Cricket Wooten, and Margy Martyn during a rehearsal for Florenz Ziegfeld’s Ziegfeld Follies revues. Fields was a Follies cast member off and on from 1915 until 1925. He was known from the beginning of his career for having a large nose, and it reddened and grew over time due to rosacea and rhinophyma. This shot is from today, 1925.
 And now for my talent I’m going to stun the room into total silence.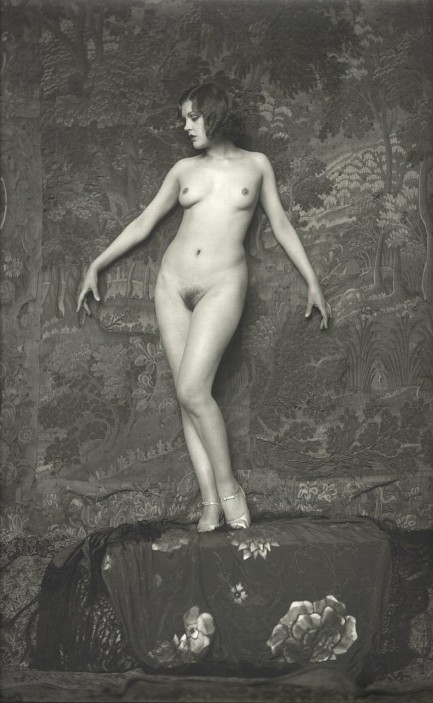 
We’re reaching a bit farther back than usual for a femme fatale with this great Alfred Cheney Johnston image of Jacqueline Schalley, aka Jacqueline Schally, a Folies Bergère and Ziegfeld dancer who was once chosen the “Fairest Girl in France.” Based on that distinction she was sent to the U.S. to do a nationwide publicity tour before competing in New York City in an international beauty pageant. No word on whether she won, but then again, the judges probably never saw her like this. Photo is from 1927.
|
 |

The headlines that mattered yesteryear.
2003—Hope Dies
Film legend Bob Hope dies of pneumonia two months after celebrating his 100th birthday. 1945—Churchill Given the Sack
In spite of admiring Winston Churchill as a great wartime leader, Britons elect
Clement Attlee the nation's new prime minister in a sweeping victory for the Labour Party over the Conservatives. 1952—Evita Peron Dies
Eva Duarte de Peron, aka Evita, wife of the president of the Argentine Republic, dies from cancer at age 33. Evita had brought the working classes into a position of political power never witnessed before, but was hated by the nation's powerful military class. She is lain to rest in Milan, Italy in a secret grave under a nun's name, but is eventually returned to Argentina for reburial beside her husband in 1974. 1943—Mussolini Calls It Quits
Italian dictator Benito Mussolini steps down as head of the armed forces and the government. It soon becomes clear that Il Duce did not relinquish power voluntarily, but was forced to resign after former Fascist colleagues turned against him. He is later installed by Germany as leader of the Italian Social Republic in the north of the country, but is killed by partisans in 1945.
|

|
|

It's easy. We have an uploader that makes it a snap. Use it to submit your art, text, header, and subhead. Your post can be funny, serious, or anything in between, as long as it's vintage pulp. You'll get a byline and experience the fleeting pride of free authorship. We'll edit your post for typos, but the rest is up to you. Click here to give us your best shot.

|
|