| Modern Pulp | Jun 12 2022 |







| Modern Pulp | Mar 24 2009 |





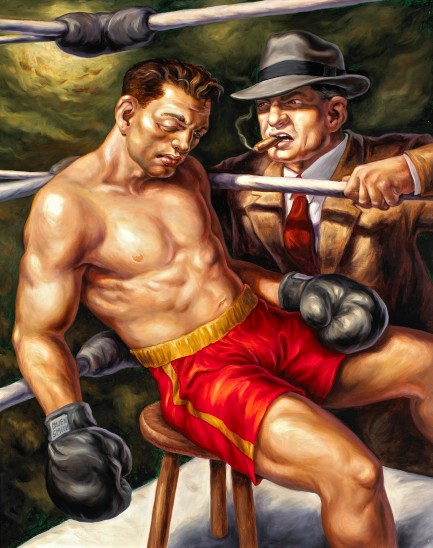
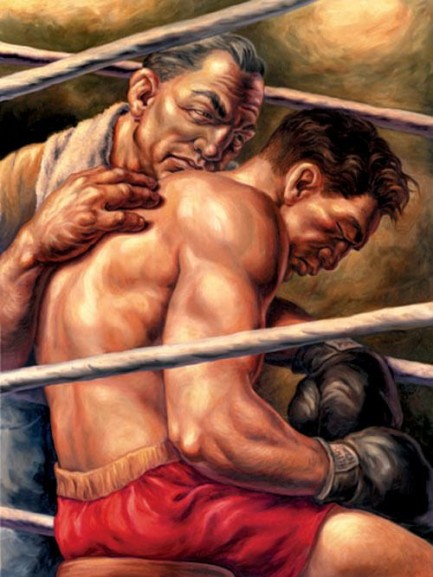
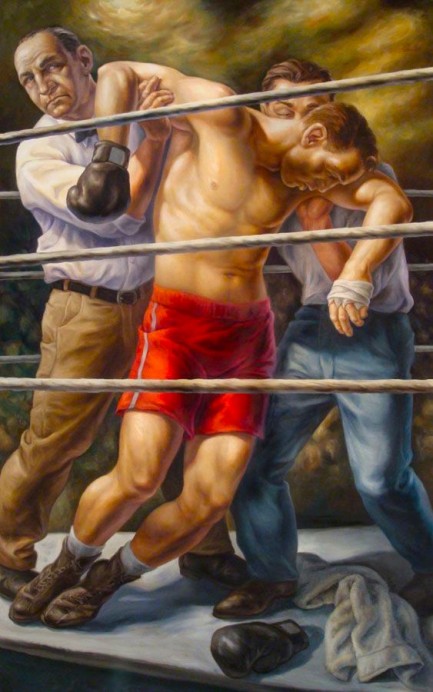
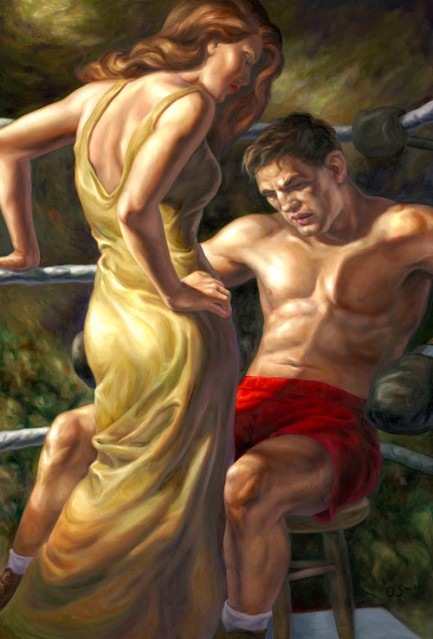
These may look like new Dashiell Hammett book covers, but they’re actually promotional posters painted by the brilliant Owen Smith for the San Francisco Arts Commission’s Art on Market Street 2008 Program. If you read our post on author Daniel Chavarría you know we love Smith’s work. When we see it we immediately think pulp, but we aren’t particularly reminded of any other pulp artist’s work. To be fair, we don’t know if Smith considers himself a pulp artist, but we do think his paintings are lurid and mysterious in way that make them a fit for the genre.
Moving on from the Hammett pieces, the painting chosen for the cover of Maureen Dowd’s Are Men Neccesary? is also great, though we don’t think it belongs on a collection of essays. Below that, The Forgotten Arm is an Aimee Mann album, and the pairing is also a bit
 square peg/round hole. If it has to be music, we’d rather see Smith’s work on a José James cd; if on a book, then where better than on the next James Ellroy? But the art remains brilliant regardless, and we look forward to Smith’s future creations. You can see more here, and the write-up we mentioned on Chavarría is here.
square peg/round hole. If it has to be music, we’d rather see Smith’s work on a José James cd; if on a book, then where better than on the next James Ellroy? But the art remains brilliant regardless, and we look forward to Smith’s future creations. You can see more here, and the write-up we mentioned on Chavarría is here.
| Modern Pulp | Jan 17 2009 |



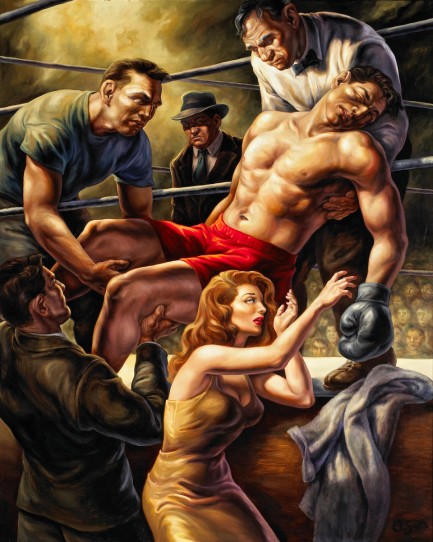
Uruguayan author Daniel Chavarría was a miner, a model, and a museum guide, before landing in Cuba and launching a literary career. He’s since won the Dashiell Hammett Award for his novel Gijón and the Edgar Award for Adios Muchachos. His fiction is political, comical, and suspenseful, but most of all it is palpably tropical, the product of a languid and overheated island where material riches are few but passions run high. Read Chavarría and you’ll immediately perceive the difference between fiction written by foreign authors who maybe spend six weeks in Cuba, and a man who has lived there for decades and calls it home. For instance, what foreign author could hope to explain the concept of bicycle hookers, and all the subtleties associated with their trade? Chavarría does exactly that in Adios Muchachos. In fact, he writes primarily about hookers. They’re his obsession, his muses, and he depicts them both unflinchingly and reverently. We won’t tell you more—except that we very much enjoyed the above two books. The English versions commissioned from Carloz Lopez and the award winning translator Peter Bush have all the flavor of the originals. And as a bonus, illustrator Owen Smith’s cover paintings serve as perfect encapsulations of the strange, dark beauty of Chavarría’s prose. More on Smith later.
| Intl. Notebook | Jan 1 2009 |

.jpg)
Fifty years ago on this day, U.S.-installed dictator Fulgencio Batista fled Cuba, acknowledging defeat by socialist forces aligned with Fidel Castro. At the time Cuba was controlled by U.S. business interests and organized crime figures, with 75% of its land in foreign hands, and the capital of Havana serving as an international vice playground. It was known as the Monte Carlo of the Caribbean, and establishments like the Tropicana, San Souci, and Shanghai Theatre were famous for casinos, prostitutes, and totally nude cabaret shows. The El Dorado had an all female orchestra. Mobster Meyer Lansky was royalty. Luminaries such as Frank Sinatra, Nat King Cole, and Edith Piaf were regular headliners. Havana was simply the place to be.
Less than an hour from Florida by air, New York businessmen who’d told their wives they were at a Miami conference could be enjoying a Cuban whore by lunchtime, and be back in Dade County in time for bed and a phone call from the missus. Alternatively, they could stay all night, or for days at a time, and lose themselves in daiquiris, dancing girls, and the lure of forbidden Barrio Colón. It was paradise—at least if you were a foreigner or one of the wealthy Cubans in partnership with them. For the poor Havana was pure hell. The billions in revenue earned by casinos and hotels trickled not down, but out—into foreign bank accounts. Malnutrition, illiteracy, and crime were rampant. When Castro ran Batista off the island the party cautiously continued, because his political intentions were not immediately clear. Everyone knew the old system would change; nobody knew exactly how much. But for a brief, post-revolutionary moment Cuba remained open to foreigners, and so the expatriate carnival went on—albeit under a cloud.
poor Havana was pure hell. The billions in revenue earned by casinos and hotels trickled not down, but out—into foreign bank accounts. Malnutrition, illiteracy, and crime were rampant. When Castro ran Batista off the island the party cautiously continued, because his political intentions were not immediately clear. Everyone knew the old system would change; nobody knew exactly how much. But for a brief, post-revolutionary moment Cuba remained open to foreigners, and so the expatriate carnival went on—albeit under a cloud.
But the lines had already been drawn in the greatest ideological battle of modern times. U.S. president Dwight D. Eisenhower was using the CIA to train Cuban exiles for an invasion to oust the socialists, and Castro was planning to nationalize a corrupt capitalist economy that had excluded those who were too poor, too black, or too lacking in influence to get a seat at the big table. When Castro made nationalization official, the U.S. struck with an embargo, and followed up five months later with the failed Bay of Pigs invasion. Since then the ideological battle lines have occasionally shifted, but Cuba remains the prize jewel of the war.
Bay of Pigs invasion. Since then the ideological battle lines have occasionally shifted, but Cuba remains the prize jewel of the war.
As historical events go, the Cuban Revolution, as well as its prelude and aftermath, have been invaluable to genre fiction, providing rich material for authors such as Graham Greene, James Ellroy and a literary who’s-who of others. It has been the subject of countless revisionist potboilers. Stephen Hunter’s Havana is perhaps the best of these novels, at least by an American writer. In that one Fidel’s fate is in the hands of a goodhearted redneck from Arkansas. Sent by the CIA, the heroic marksman is more than a match for the hapless Cubans, but does he really want to kill Castro?
Daniel Chevarría went Hunter one better and wrote several novels set in Cuba, including Tango for a Torturer and the award winner Adios Muchachos. Movies ranging from Errol Flynn’s piece-of-fluff Cuban Rebel Girls, to Wim Wenders’ inspiring Buena Vista Social Club, to Benicio del Toro’s heavyweight Ché have also used the island as a backdrop. Doubtless Cuba will provide material for as long as authors write and directors yell action, as its history continues to inspire, and its future continues to be in flux.