| The Naked City | Jan 12 2024 |


Police Lt. Hugh Crowley lies dead in the Fox Westwood Village Theater in Los Angeles after being shot today in 1932. Crowley had gone to the theater after closing time to retrieve box office receipts, but instead surprised two thieves. Crowley reached for his sidearm and fired, and one of the crooks gunned him down. Both men were captured and tried, and Joseph Francis Regan, who had fired the fatal shot and actually been hit in the abdomen by a bullet fired by Crowley, was sentenced to death. Jack Green, who had no prior criminal record, had not fired a shot, and had cooperated in the police investigation, nevertheless also was sentenced to death, probably because he had planned the crime. Regan was hanged at San Quentin State Prison in August 1933. Green came close to the gallows, but received numerous reprieves after public pleas for leniency from his parents, and rulings from higher courts. Eventually his sentence was commuted to life in prison.
Although Green was probably never aware of it, legal authorities often cited his case during the long battle over the constitutionality of the death penalty in California. The idea put forth by the pro-death penalty side around 1960 was that even though Green’s commuted sentence specified “without possibility of parole,” there was no actual reason in California jurisprudence or the state constitution that he could not be released. All that was required was for an appropriate state authority to decide to do it. They felt therefore that anti-death penalty campaigners’ assurances that criminals could be imprisoned for life if such punishment was deemed necessary meant nothing. No matter the language of the original life sentence, any criminal could later be released. Green doubtless would have found all this fascinating, but none of it ever came to affect him. As far as we can tell, he did in fact spend the rest of his life in San Quentin.
| The Naked City | May 2 2017 |


Caryl Chessman and a detective named E.M. Goossen appear in the above photo made shortly after Chessman's arrest in January of 1948. Chessman had robbed several victims in the Los Angeles area, two of whom were women that he sexually assaulted. He forced one woman to perform oral sex on him, and did the same to the other in addition to anally raping her. Chessman was convicted under California's Little Lindbergh Law, named after Charles Lindbergh's infamously kidnapped and murdered son. The law specifically covered intrastate acts of abduction in which victims were physically harmed, two conditions that made the crime a potentially capital offense.

| Vintage Pulp | Aug 4 2016 |


 Set initially at San Quentin Prison, then in the wider environs of Oakland, California, I'll Get Mine follows a do-gooder prison shrink down the rabbit hole of Latino gang culture, where he becomes involved in a murder mystery and takes on the role of potential savior to a beautiful druggie ensnared in Pachuco culture. It was originally published in 1951 as Cure It with Honey, which you see at right.
Set initially at San Quentin Prison, then in the wider environs of Oakland, California, I'll Get Mine follows a do-gooder prison shrink down the rabbit hole of Latino gang culture, where he becomes involved in a murder mystery and takes on the role of potential savior to a beautiful druggie ensnared in Pachuco culture. It was originally published in 1951 as Cure It with Honey, which you see at right.| The Naked City | May 26 2011 |


This May 1973 issue of the true crime magazine Master Detective delves back more than four decades to examine one of the most infamous murders committed in early twentieth century America. The victim was a 12-year old Los Angeles girl named Marion Parker, and on December 15, 1927, she was abducted from her school by a man who used to work for her father. The man—nineteen-year-old William Edward Hickman—came to the school and told the registrar that the girl’s father had been in an accident that morning and wished to see his daughter. It was not policy to release children to anyone other than their parents, but swayed by Hickman’s measured urgency and apparent sincerity, the registrar released Marion Parker into his custody.
Hickman was after money. Marion Parker’s father, a banker named Perry Parker, had it in abundance. For the next few days Hickman sweated Perry Parker, sending pleading notes written by Marion, as well as other notes demanding a ransom. Hickman signed the latter with various pseudonyms, but one in particular stuck with the press—“The Fox.” Eventually, Parker and Hickman agreed on a ransom of $1,500, to be paid  in $20 gold certificates. The first attempt at an exchange failed when Hickman noticed a cop near the meeting place. It’s unclear whether the policeman was part of a trap, but Hickman was taking no chances. He bailed, and set up a second meeting for a few nights later.
in $20 gold certificates. The first attempt at an exchange failed when Hickman noticed a cop near the meeting place. It’s unclear whether the policeman was part of a trap, but Hickman was taking no chances. He bailed, and set up a second meeting for a few nights later.
When Parker reached the rendezvous point he saw Hickman sitting in a parked car. Parker approached the driver side window and saw that the kidnapper was aiming a gun, and he also saw his daughter in the passenger seat, bundled up to her neck in a blanket. She couldn’t move—that was clear. She didn’t speak. Hickman took the ransom and drove quickly away, stopping just long enough to push Marion Parker out of the car at the end of the block. When Parker reached his daughter and lifted her into his arms he screamed in anguish. Marion was dead, and had been for twelve hours. Hickman had cut off her arms and legs, flayed the skin from her back, disemboweled her, and stuffed her with rags. She had been bundled up to conceal the fact that she had no limbs. Her eyes had been wired open so that she would, upon cursory inspection, appear to be alive.
Hickman had escaped, but he had left behind a clue that would lead to his capture. Among the rags he had stuffed into Marion Parker’s empty abdomen was a shirt with a laundry mark that police were able to trace to an address in Los Angeles. Twenty cops descended on a residence that turned out to be occupied by a man named Donald Evans, who was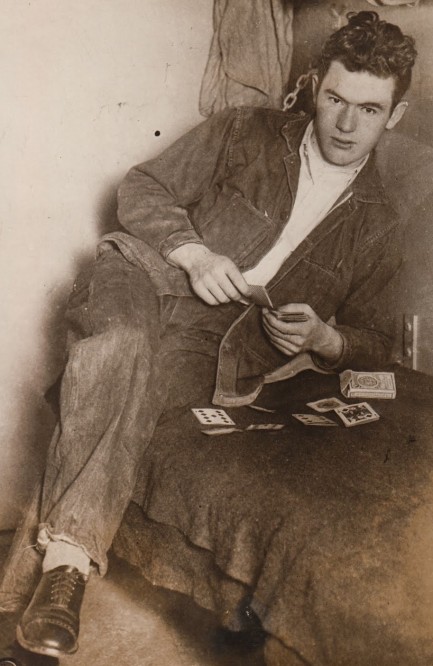 cooperative but said he knew nothing about Hickman. In truth Evans was Hickman, but by the time police figured that out he had fled to the Pacific Northwest. But he hadn’t run far enough. Wanted posters reached every corner of the west coast within days, and just one week after Hickman’s disappearance two police officers in the town of Echo, Oregon recognized him and arrested him.
cooperative but said he knew nothing about Hickman. In truth Evans was Hickman, but by the time police figured that out he had fled to the Pacific Northwest. But he hadn’t run far enough. Wanted posters reached every corner of the west coast within days, and just one week after Hickman’s disappearance two police officers in the town of Echo, Oregon recognized him and arrested him.
At trial, Hickman claimed to be guided by voices—one of the first times, if not the first, that this type of insanity defense was attempted in an American courtroom. But the jury wasn’t buying any of it and they convicted Hickman of murder and kidnapping. The judge sentenced him to be executed at San Quentin State Prison, and he climbed the stairs to the gallows on October 19, 1928. Hickman had once been smooth enough to talk a school official into sending Marion Parker to her doom, and had calmly lied about his identity to twenty cops who had burst into his house. In prison he had corresponded with and impressed author Ayn Rand so much that she decided to base a character on him because he embodied her mythical “Nietzschean Superman” ideal. But at the end, all of Hickman’s considerable aplomb deserted him. Just before the hangman sprang the trapdoor that would cast him into oblivion, he collapsed babbling in fear. His last words were, “Oh my God! Oh my God!”